- Home
- Products
- Applications
- Capacitors for Household Appliances
- Capacitors for Power Supply
- Capacitors for LED Lighting
- Capacitors for Mobile And DSL Appliances
- Capacitors for Automotive& Vehicles
- Capacitors for Photovoltaic Inverters
- Capacitors for Wind Power Plants
- Capacitors for Renewable Energy Systems
- Capacitors for Induction Heating
- Capacitors for Medical Equipments
- Capacitors for Industrial Control
- Capacitors for Power Electric
- Capacitors for Rail Transit
- Capacitors for Smart Grid
- Capacitors for University & Research Instituite (High Energy Physics)
- About Us
- News
- Contact Us
-
- Capacitors for Household Appliances
- Capacitors for Power Supply
- Capacitors for LED Lighting
- Capacitors for Mobile And DSL Appliances
- Capacitors for Automotive& Vehicles
- Capacitors for Photovoltaic Inverters
- Capacitors for Wind Power Plants
- Capacitors for Renewable Energy Systems
- Capacitors for Induction Heating
- Capacitors for Medical Equipments
- Capacitors for Industrial Control
- Capacitors for Power Electric
- Capacitors for Rail Transit
- Capacitors for Smart Grid
- Capacitors for University & Research Instituite (High Energy Physics)
Web Menu
- Home
- Products
- Applications
- Capacitors for Household Appliances
- Capacitors for Power Supply
- Capacitors for LED Lighting
- Capacitors for Mobile And DSL Appliances
- Capacitors for Automotive& Vehicles
- Capacitors for Photovoltaic Inverters
- Capacitors for Wind Power Plants
- Capacitors for Renewable Energy Systems
- Capacitors for Induction Heating
- Capacitors for Medical Equipments
- Capacitors for Industrial Control
- Capacitors for Power Electric
- Capacitors for Rail Transit
- Capacitors for Smart Grid
- Capacitors for University & Research Instituite (High Energy Physics)
- About Us
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
Analysis of Capacitor Impedance and ESR Frequency Characteristics

Analysis of Capacitor Impedance and ESR Frequency Characteristics
1. Introduction
The frequency characteristics of a capacitor's impedance (|Z|) and equivalent series resistance (ESR) are critical for evaluating its performance in circuit design, particularly in noise suppression and voltage stabilization. This article systematically explains these characteristics by comparing ideal and real capacitors, supported by formulas and graphs.
2. Ideal Capacitor Behavior
An ideal capacitor's impedance is purely capacitive:
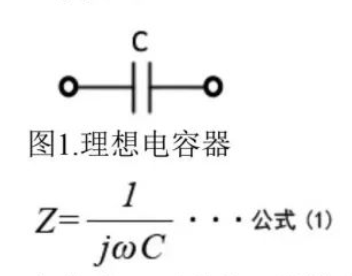
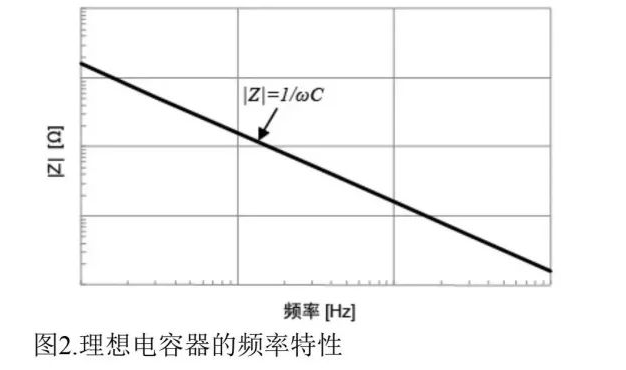
where ω is angular frequency and Cis capacitance. As shown in Figure 1,∣Z∣decreases inversely with frequency (Figure 2), and ESR is zero (no losses).
3. Real Capacitor Behavior
Real capacitors exhibit parasitic effects (Figure 3):
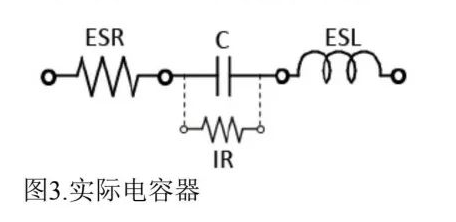
ESR: Caused by dielectric loss and electrode resistance.
ESL: Parasitic inductance from electrodes or leads.
Their frequency response follows a V-curve (Figure 4):
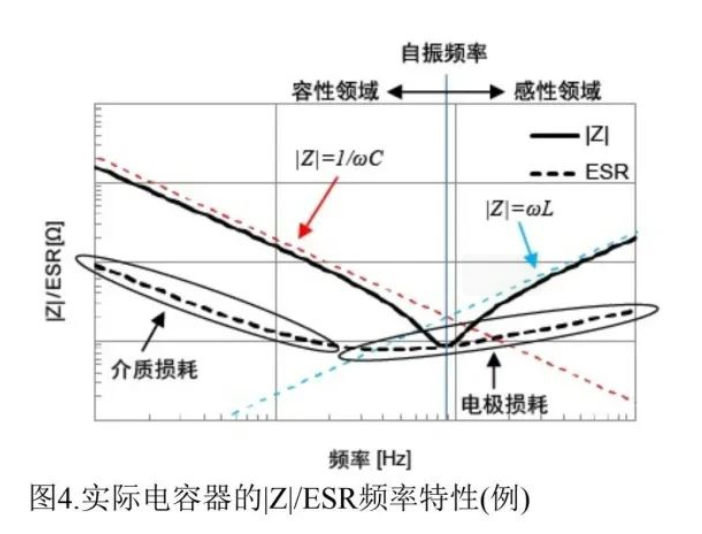
Low-frequency range (Capacitive region): ∣Z∣=1/ωC, ESR dominated by dielectric loss.
Resonance point:∣Z∣reaches minimum (∣Z∣=ESR), defining the self-resonant frequency.
High-frequency range (Inductive region):∣Z∣=ωL, ESR affected by skin effect.
4. Comparison of Capacitor Types
For 10μF capacitors (Figure 5):
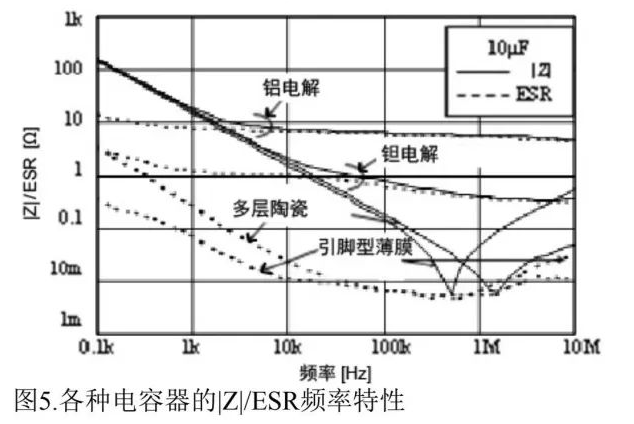
Aluminum electrolytic: High ESR at high frequencies (due to electrolyte resistivity).
Multilayer ceramic: Excellent high-frequency performance with low ESR.
Film capacitors: Low ESL, ideal for high-frequency applications.
5. Conclusion
In high-frequency circuits, ESR and ESL must be carefully considered. Designers should select capacitors based on frequency requirements, such as multilayer ceramics for decoupling and aluminum electrolytics for low-frequency filtering.

 简体中文
简体中文 English
English Español
Español