- Home
- Products
- Applications
- Capacitors for Household Appliances
- Capacitors for Power Supply
- Capacitors for LED Lighting
- Capacitors for Mobile And DSL Appliances
- Capacitors for Automotive& Vehicles
- Capacitors for Photovoltaic Inverters
- Capacitors for Wind Power Plants
- Capacitors for Renewable Energy Systems
- Capacitors for Induction Heating
- Capacitors for Medical Equipments
- Capacitors for Industrial Control
- Capacitors for Power Electric
- Capacitors for Rail Transit
- Capacitors for Smart Grid
- Capacitors for University & Research Instituite (High Energy Physics)
- About Us
- News
- Contact Us
-
- Capacitors for Household Appliances
- Capacitors for Power Supply
- Capacitors for LED Lighting
- Capacitors for Mobile And DSL Appliances
- Capacitors for Automotive& Vehicles
- Capacitors for Photovoltaic Inverters
- Capacitors for Wind Power Plants
- Capacitors for Renewable Energy Systems
- Capacitors for Induction Heating
- Capacitors for Medical Equipments
- Capacitors for Industrial Control
- Capacitors for Power Electric
- Capacitors for Rail Transit
- Capacitors for Smart Grid
- Capacitors for University & Research Instituite (High Energy Physics)
Web Menu
- Home
- Products
- Applications
- Capacitors for Household Appliances
- Capacitors for Power Supply
- Capacitors for LED Lighting
- Capacitors for Mobile And DSL Appliances
- Capacitors for Automotive& Vehicles
- Capacitors for Photovoltaic Inverters
- Capacitors for Wind Power Plants
- Capacitors for Renewable Energy Systems
- Capacitors for Induction Heating
- Capacitors for Medical Equipments
- Capacitors for Industrial Control
- Capacitors for Power Electric
- Capacitors for Rail Transit
- Capacitors for Smart Grid
- Capacitors for University & Research Instituite (High Energy Physics)
- About Us
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
Submit feedback
Metallized Film Capacitors: A Comprehensive Guide
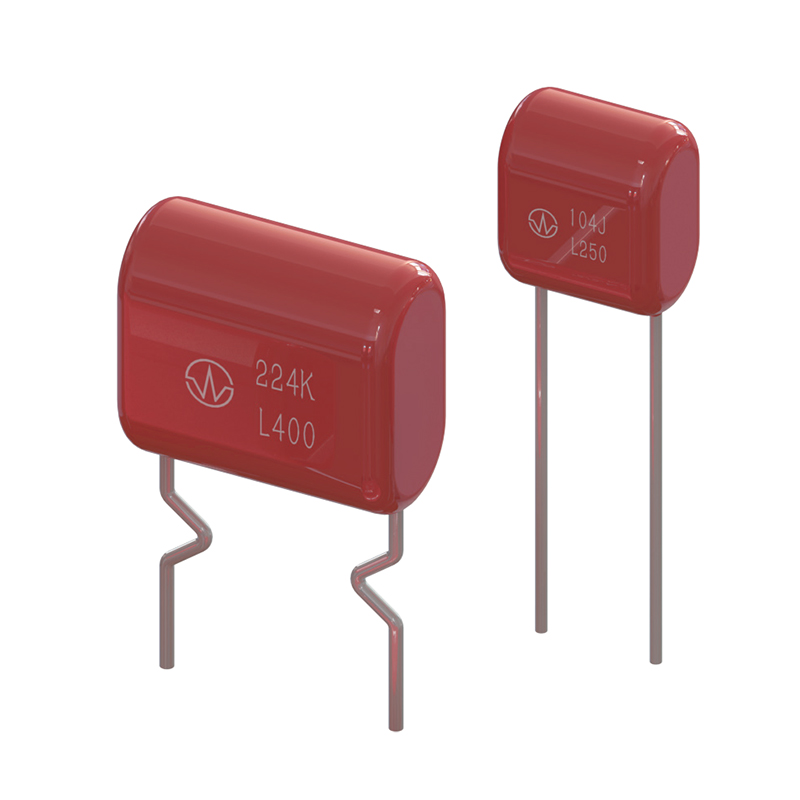

Metallized Film Capacitors: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Metallized Film Capacitors
In modern power electronics, the metallized film capacitor plays a vital role due to its high stability, reliability, and long operational lifespan. Unlike traditional electrolytic or ceramic capacitors, this component uses a thin dielectric plastic film coated with a metal layer, such as aluminum or zinc, which provides self-healing capabilities and high voltage resistance. These advantages make it a preferred choice in applications like DC link capacitors, lighting systems, and renewable energy converters.
What Are Metallized Film Capacitors?
A metallized film capacitor is constructed by depositing a very thin metal layer on one or both sides of a plastic dielectric film. The metallization serves as the electrode, while the dielectric film—commonly polypropylene (PP), polyester (PET), or polyethylene naphthalate (PEN)—determines the capacitor’s electrical and thermal characteristics.
The distinctive feature of a metallized film capacitor is its self-healing ability. When a dielectric breakdown occurs due to overvoltage or impurities, the localized heat evaporates the metal layer around the fault point. This isolates the defect and restores the capacitor’s functionality almost instantly, extending its service life significantly.
Types of Metallized Film Capacitors
Different dielectric materials define distinct capacitor characteristics and application fields:
| Type | Dielectric Material | Key Properties | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metallized Polypropylene (MPP) | Polypropylene | Low ESR, high ripple current, stable over temperature | DC link capacitors, power supplies |
| Metallized Polyester (PET) | Polyester | High volumetric efficiency, cost-effective | Lighting ballasts, general electronics |
| Metallized Polyethylene Naphthalate (PEN) | PEN | High temperature resistance | Automotive and industrial electronics |
| Metallized Polystyrene (PS) | Polystyrene | High precision, low loss | Audio and measurement circuits |
| Others (PPS, PTFE) | Varies | Excellent thermal and electrical performance | High-end industrial use |
Among these, the metallized polypropylene capacitor is the widely used for DC link applications because of its low dielectric losses and self-healing capability.
Construction and Manufacturing
The performance of a film capacitor depends heavily on its manufacturing precision. The process includes:
Film Deposition: A metal layer is vapor-deposited onto the dielectric film under vacuum conditions.
Winding: The metallized film is wound into a compact cylindrical or oval shape, optimizing surface area and electrical path.
Encapsulation: The wound core is encapsulated in resin or epoxy for moisture protection and mechanical strength.
Testing: Parameters such as capacitance, ESR, insulation resistance, and dielectric integrity are rigorously inspected to ensure reliability.
Key Parameters and Specifications
When selecting or designing a metallized film capacitor, several key electrical parameters define its performance:
| Parameter | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitance | Ability to store charge | Determines energy density |
| ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) | Internal resistance of the capacitor | Affects power dissipation and heating |
| ESL (Equivalent Series Inductance) | Internal inductance | Impacts high-frequency performance |
| Voltage Rating | Maximum safe voltage | Ensures safe operation in power systems |
| Dissipation Factor (DF) | Loss ratio under AC conditions | Indicates energy efficiency |
| Insulation Resistance | Leakage resistance | Defines long-term reliability |
For DC link capacitor applications, a low ESR and high voltage rating are critical to maintain energy efficiency and stability during power conversion.
Advantages of Metallized Film Capacitors
The metallized film capacitor offers multiple advantages that make it to other technologies in various scenarios:
Self-Healing Property: Automatically isolates damaged sections to restore performance.
High Stability: Minimal capacitance drift under temperature or voltage stress.
Low ESR and ESL: Ensures high-frequency capability and low power loss.
High Voltage Handling: Suitable for high-current circuits.
Extended Lifespan: Ideal for continuous-duty environments such as industrial drives or solar inverters.
Disadvantages of Metallized Film Capacitors
While their performance is excellent, a few limitations exist:
Larger Size: Compared to ceramic capacitors with the same capacitance.
Humidity Sensitivity: Certain dielectric materials, such as PET, can degrade in humid environments without adequate sealing.
Higher Cost: Some high-performance types (like PEN or PPS) are more expensive due to material complexity.
Applications of Metallized Film Capacitors
Metallized film capacitors are widely utilized in systems where reliability and power handling are critical:
Power Electronics: Used as DC link capacitors to smooth and store energy in converters and inverters.
Motor Control Systems: Provide noise suppression and energy buffering.
Lighting Ballasts: Regulate current and improve power factor.
Audio Equipment: Ensure low distortion and stable frequency response.
Renewable Energy Systems: Support voltage stability and transient suppression in photovoltaic and wind power converters.
Comparison with Other Capacitor Technologies
| Feature | Metallized Film Capacitor | Ceramic Capacitor | Electrolytic Capacitor | Tantalum Capacitor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dielectric | Polymer film | Ceramic | Electrolyte | Tantalum oxide |
| Self-Healing | Yes | No | No | No |
| ESR | Low | Moderate | High | Moderate |
| Voltage Range | Wide | Limited | Wide | Limited |
| Stability | Excellent | High | Poor | Good |
| Typical Use | DC link, power electronics | RF circuits | Filtering | Compact circuits |
The metallized film capacitor provides the balance between performance, reliability, and self-healing functionality, making it indispensable in high-power and precision applications.
Future Trends in Metallized Film Capacitors
As industries push for higher efficiency and compactness, several development trends are shaping the future of film capacitor design:
Miniaturization: Advances in film thickness and metallization technology reduce size without compromising performance.
High-Temperature Operation: Development of new dielectrics like PEN and PPS enables use in harsher environments.
Enhanced Self-Healing: Improved metallization control leads to better fault isolation and longer operational life.
Eco-Friendly Materials: Research focuses on recyclable and halogen-free film materials to meet environmental standards.
Safety Considerations
In power circuits, safety is paramount. Proper derating, thermal management, and overvoltage protection are essential to prevent breakdown. The following guidelines are commonly applied:
Operate below 80% of rated voltage for long-term reliability.
Ensure adequate cooling to prevent film degradation.
Use surge suppressors in DC link circuits to handle transient spikes.
Conclusion
The self-healing property remains the defining characteristic that sets the metallized film capacitor apart from other capacitor types. Its ability to restore functionality after electrical stress ensures high reliability in demanding power electronic systems. From DC link capacitors in renewable energy converters to precision PET capacitors in consumer electronics, film capacitor technology continues to evolve toward higher performance, improved thermal endurance, and environmental sustainability.

 简体中文
简体中文 English
English Español
Español