- Home
- Products
- Applications
- Capacitors for Household Appliances
- Capacitors for Power Supply
- Capacitors for LED Lighting
- Capacitors for Mobile And DSL Appliances
- Capacitors for Automotive& Vehicles
- Capacitors for Photovoltaic Inverters
- Capacitors for Wind Power Plants
- Capacitors for Renewable Energy Systems
- Capacitors for Induction Heating
- Capacitors for Medical Equipments
- Capacitors for Industrial Control
- Capacitors for Power Electric
- Capacitors for Rail Transit
- Capacitors for Smart Grid
- Capacitors for University & Research Instituite (High Energy Physics)
- About Us
- News
- Contact Us
-
- Capacitors for Household Appliances
- Capacitors for Power Supply
- Capacitors for LED Lighting
- Capacitors for Mobile And DSL Appliances
- Capacitors for Automotive& Vehicles
- Capacitors for Photovoltaic Inverters
- Capacitors for Wind Power Plants
- Capacitors for Renewable Energy Systems
- Capacitors for Induction Heating
- Capacitors for Medical Equipments
- Capacitors for Industrial Control
- Capacitors for Power Electric
- Capacitors for Rail Transit
- Capacitors for Smart Grid
- Capacitors for University & Research Instituite (High Energy Physics)
Web Menu
- Home
- Products
- Applications
- Capacitors for Household Appliances
- Capacitors for Power Supply
- Capacitors for LED Lighting
- Capacitors for Mobile And DSL Appliances
- Capacitors for Automotive& Vehicles
- Capacitors for Photovoltaic Inverters
- Capacitors for Wind Power Plants
- Capacitors for Renewable Energy Systems
- Capacitors for Induction Heating
- Capacitors for Medical Equipments
- Capacitors for Industrial Control
- Capacitors for Power Electric
- Capacitors for Rail Transit
- Capacitors for Smart Grid
- Capacitors for University & Research Instituite (High Energy Physics)
- About Us
- News
- Contact Us
Product Search
Exit Menu
Characteristics and applications of safety capacitors
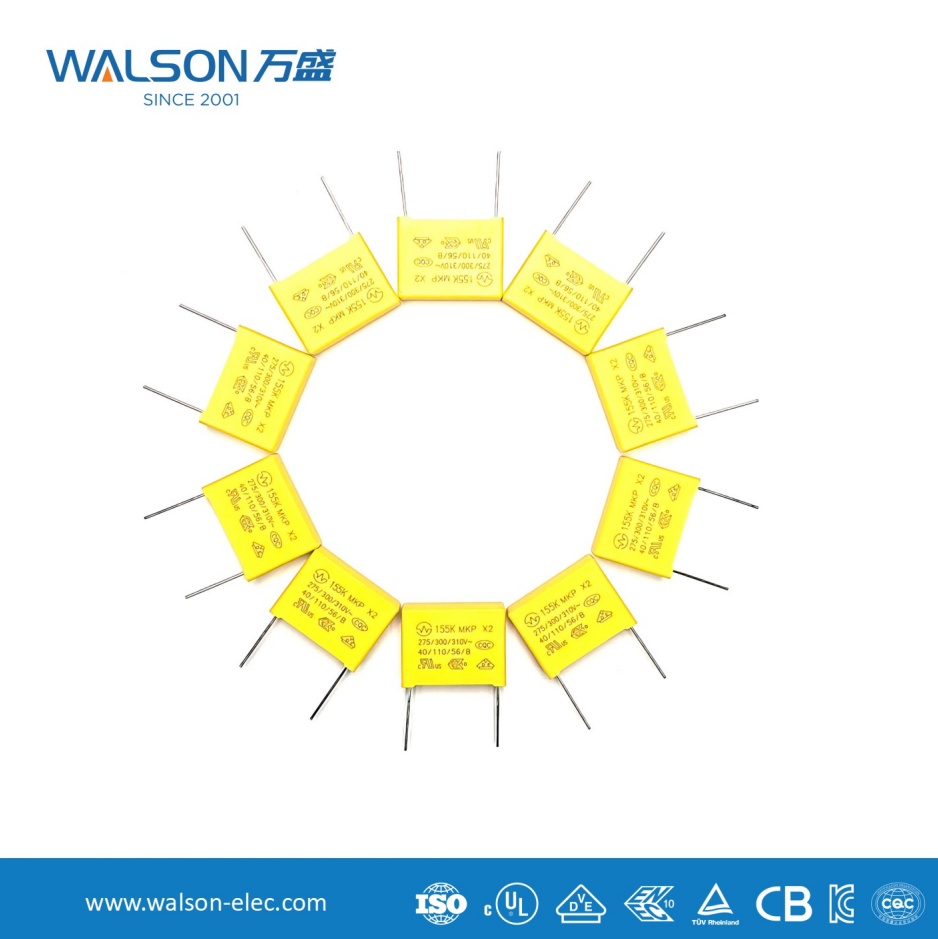
Characteristics and applications of safety capacitors
I. Core Characteristics (Essential Differences from Ordinary Capacitors)
The characteristics of safety capacitors revolve around the word “safety”:
1. Failure Mode Safety
Key characteristic: This is the crucial feature of safety capacitors. When a capacitor fails due to overvoltage, overheating, or other reasons, it is designed to operate in an open-circuit mode, rather than a short-circuit mode.
Why is this important?
If a capacitor connected between the live and neutral wires (X capacitor) or between the live/neutral wire and ground (Y capacitor) fails due to a short circuit, it can electric shock, fire, or equipment damage. An open-circuit failure, however, only results in the loss of its filtering function and will not cause a safety hazard.
2. Employing Metallized Thin-Film Dielectric
Polypropylene (MKP) or polyester film is typically used. This medium has self-healing properties: when the film is partially broken down, the heat generated at the breakdown point causes the surrounding metal plating to evaporate, thereby isolating the fault point, allowing the capacitor to partially restore its function and remain in an open circuit state instead of being permanently short-circuited.
3. High Standard of Pressure Resistance and Impact Resistance
- High rated voltage: Typically available in 250VAC, 275VAC, 310VAC, 440VAC, etc.
- High surge voltage resistance: It can withstand instantaneous high-voltage pulses (such as lightning strikes and switching surges) far exceeding the operating voltage. For example, an X1 capacitor may need to withstand a 4kV pulse voltage.
- High insulation resistance: Ensures minimal leakage current, which is especially crucial for Y capacitors.
4. Mandatory Security Certification
Safety capacitors must obtain security certification from the country or region where they are used, such as:
- China: CQC (the security component of CCC certification)
- North America: UL (United States), cUL (Canada)
- Europe: VDE (Germany), ENEC (European common standard)
The certification mark is printed directly on the capacitor body, which is the intuitive identification basis when purchasing.
II. Classification and Application
Safety capacitors are mainly classified into X capacitors and Y capacitors based on their connection location and protection level.
| Type | Connection Location | Main Function | Security Level (Common) | Application Scenarios and Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| X Capacitor | Connected between the live wire (L) and the neutral wire (N). | Differential-mode filtering suppresses symmetrical interference between power lines. | X1 > X2 > X3 | X1: Suitable for high-pulse applications (industrial equipment and products with high reliability), Peak pulse voltage ≥ 4kV. X2 (Most common): Suitable for general electronic equipment, household appliances, power supplies, etc. Peak pulse voltage ≥ 2.5kV. X3: For applications with lower safety requirements. |
| Y Capacitor | Connect between the live wire (L) and ground (G) or the neutral wire (N) and ground (G). | Common-mode filtering suppresses asymmetric interference between the line and ground. It provides a high-frequency path and reduces EMI. | Y1 > Y2 > Y3 > Y4 | Y1 (Highest Class): Double insulation, withstands high voltage ≥8kV. Commonly used in medical equipment and high-reliability equipment. Y2 (Most Common): Basic insulation, withstands high voltage ≥5kV. Widely used in home appliances, IT equipment, and power adapters. Y3 / Y4: Used in applications with lower safety requirements. |
III. Selection and Usage Guidelines
1. Determine the Type Based on the Application Location
- Use an X capacitor between L and N; use a Y capacitor between L/PG or N/PG. Never interchange them or substitute with ordinary capacitors.
2. Select the Safety Level According to Safety Standards
- For equipment with strict requirements on ground leakage current (such as medical devices and handheld devices), Y1 should be selected.
- Y2 is recommended for general household appliances and IT equipment.
- For environments with high input voltage and severe lightning surges (such as outdoor equipment), consider X1; for general indoor use, use X2.
3. Focus on Key Parameters
- Rated voltage: Must be higher than the circuit’s AC operating voltage.
- Capacitance: Common values for X capacitors are 0.1μF, 0.22μF, 0.47μF, etc.; Y capacitors have smaller capacitance (usually ≤ a few nF) to control leakage current.
- Safety certification: Confirm whether the required certification marks are present in the target market.
4. Pay Attention to the Usage Guidelines
- X capacitors: Because the stored charge after power is cut off may cause electric shock, X capacitors with a capacitance greater than 0.1μF must be connected in parallel with a discharge resistor (usually in the megohm range) to ensure that the voltage is reduced to a safe value within a specified time (e.g., within 1 second).
- Y capacitors: When wiring, the leads should be as short as possible and placed close to the ground terminal of the filter to enhance the high-frequency filtering effect. Multiple Y capacitors should be grounded at the same point (“clean ground”).
Summary
Safety capacitors are guardians of safety and EMC compliance in power supply design. Their essence is to prioritize user safety both in the event of failure and during operation (filtering). Proper selection and use of X and Y capacitors are indispensable for any electronic device connected to the power grid to pass safety certifications (such as CCC, UL, CE) and electromagnetic compatibility tests. They must be treated as safety devices, not ordinary filtering components, during the design process.

 简体中文
简体中文 English
English Español
Español